Настроим автозапуск сервера Seafile при загрузке системы.
https://download.seafile.com/published/seafile-manual/deploy/start_seafile_at_system_bootup.md
Для systemd
Debian 8 и старше, Linux Ubuntu 15.04 и старше
${seafile_dir} — измените переменную на путь к вашей директории Seafile.
Работаем под рутом. Создаём сервис seafile:
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/seafile.serviceСодержимое:
[Unit]
Description=Seafile
# add mysql.service or postgresql.service depending on your database to the line below
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest/seafile.sh start
ExecStop=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest/seafile.sh stop
LimitNOFILE=infinity
User=seafile
Group=seafile
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetСоздаём сервис seahub:
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/seahub.serviceСодержимое:
[Unit]
Description=Seafile hub
After=network.target seafile.service
[Service]
Environment="LC_ALL=ru_RU.UTF-8"
Type=simple
# change start to start-fastcgi if you want to run fastcgi
ExecStart=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest/seahub.sh start
ExecStop=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest/seahub.sh stop
User=seafile
Group=seafile
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetИли (по-разному для разных версий Seafile):
[Unit]
Description=Seafile hub
After=network.target seafile.service
[Service]
Environment="LC_ALL=ru_RU.UTF-8"
Type=forking
# change start to start-fastcgi if you want to run fastcgi
ExecStart=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest/seahub.sh start
ExecStop=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest/seahub.sh stop
User=seafile
Group=seafile
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetЕсли seahub останавливается после запуска, меняем тип на forking:
[Service]
Type=forkingЗапускаем сервисы и настраиваем автозагрузку:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start seafile
systemctl start seahub
systemctl enable seafile
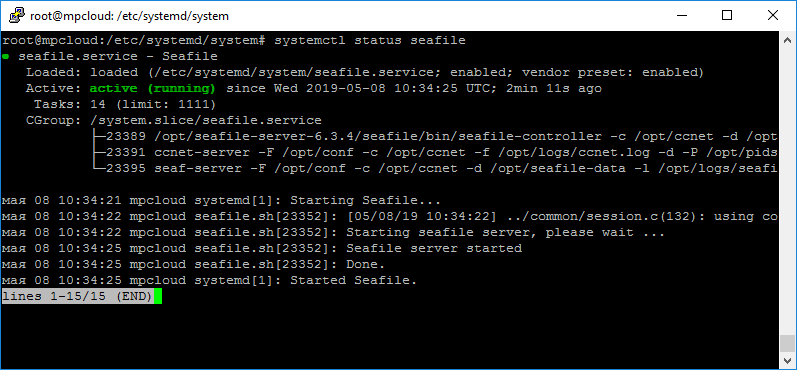
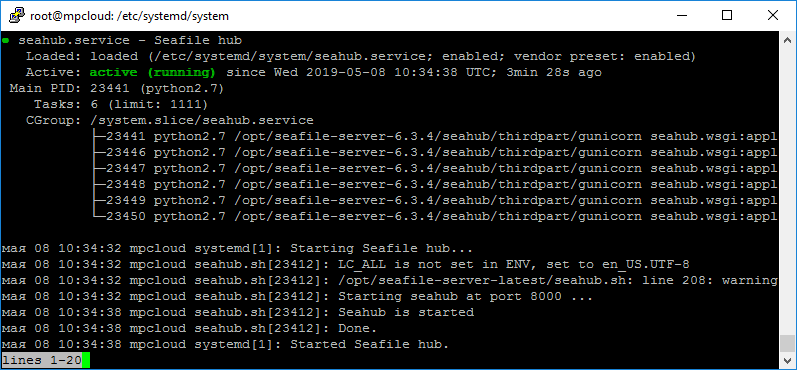
systemctl enable seahubПроверяем:
systemctl status seafilesystemctl status seahubЕсли вы используете seafile console client, то понадобится ещё один сервис seafile-client.
vim /etc/systemd/system/seafile-client.serviceСодержимое:
[Unit]
Description=Seafile client
# Uncomment the next line you are running seafile client on the same computer as server
# After=seafile.service
# Or the next one in other case
# After=network.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/usr/bin/seaf-cli start
ExecStop=/usr/bin/seaf-cli stop
RemainAfterExit=yes
User=seafile
Group=seafile
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetВключаем автозагрузку сервисов:
sudo systemctl enable seafile.service
sudo systemctl enable seahub.service
sudo systemctl enable seafile-client.service # optionalДля init.d
Ubuntu 14.10 и старше
Для Ubuntu без systemd нужно использовать /etc/init.d/ скрипты.
Создаём скрипт seafile-server:
sudo vim /etc/init.d/seafile-serverСодержимое:
#!/bin/bash
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: seafile-server
# Required-Start: $remote_fs $syslog
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs $syslog
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Seafile server
# Description: Start Seafile server
### END INIT INFO
# Change the value of "user" to your linux user name
user=haiwen
# Change the value of "seafile_dir" to your path of seafile installation
# usually the home directory of $user
seafile_dir=/data/haiwen
script_path=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest
seafile_init_log=${seafile_dir}/logs/seafile.init.log
seahub_init_log=${seafile_dir}/logs/seahub.init.log
# Change the value of fastcgi to false if fastcgi is not used
fastcgi=true
# Set the port of fastcgi, default is 8000. Change it if you need different.
fastcgi_port=8000
#
# Write a polite log message with date and time
#
echo -e "\n \n About to perform $1 for seafile at `date -Iseconds` \n " >> ${seafile_init_log}
echo -e "\n \n About to perform $1 for seahub at `date -Iseconds` \n " >> ${seahub_init_log}
case "$1" in
start)
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seafile.sh ${1} >> ${seafile_init_log}
if [ $fastcgi = true ];
then
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1}-fastcgi ${fastcgi_port} >> ${seahub_init_log}
else
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1} >> ${seahub_init_log}
fi
;;
restart)
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seafile.sh ${1} >> ${seafile_init_log}
if [ $fastcgi = true ];
then
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1}-fastcgi ${fastcgi_port} >> ${seahub_init_log}
else
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1} >> ${seahub_init_log}
fi
;;
stop)
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1} >> ${seahub_init_log}
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seafile.sh ${1} >> ${seafile_init_log}
;;
*)
echo "Usage: /etc/init.d/seafile-server {start|stop|restart}"
exit 1
;;
esacЕсли используете mysql сервер, то замените # Required-Start: $remote_fs $syslog на # Required-Start: $remote_fs $syslog mysql.
Даём права на выполнение скрипта:
sudo chmod +x /etc/init.d/seafile-serverДобавляем seafile-server в rc.d:
sudo update-rc.d seafile-server defaultsДругие Debian-based дистрибутивы
Создаём скрипт seafile-server:
sudo vim /etc/init.d/seafile-serverСодержимое:
#!/bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: seafile-server
# Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network
# Required-Stop: $local_fs
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Starts Seafile Server
# Description: starts Seafile Server
### END INIT INFO
# Change the value of "user" to linux user name who runs seafile
user=haiwen
# Change the value of "seafile_dir" to your path of seafile installation
# usually the home directory of $user
seafile_dir=/data/haiwen
script_path=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest
seafile_init_log=${seafile_dir}/logs/seafile.init.log
seahub_init_log=${seafile_dir}/logs/seahub.init.log
# Change the value of fastcgi to true if fastcgi is to be used
fastcgi=false
# Set the port of fastcgi, default is 8000. Change it if you need different.
fastcgi_port=8000
#
# Write a polite log message with date and time
#
echo -e "\n \n About to perform $1 for seafile at `date -Iseconds` \n " >> ${seafile_init_log}
echo -e "\n \n About to perform $1 for seahub at `date -Iseconds` \n " >> ${seahub_init_log}
case "$1" in
start)
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seafile.sh ${1} >> ${seafile_init_log}
if [ $fastcgi = true ];
then
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1}-fastcgi ${fastcgi_port} >> ${seahub_init_log}
else
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1} >> ${seahub_init_log}
fi
;;
restart)
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seafile.sh ${1} >> ${seafile_init_log}
if [ $fastcgi = true ];
then
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1}-fastcgi ${fastcgi_port} >> ${seahub_init_log}
else
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1} >> ${seahub_init_log}
fi
;;
stop)
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh ${1} >> ${seahub_init_log}
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seafile.sh ${1} >> ${seafile_init_log}
;;
*)
echo "Usage: /etc/init.d/seafile-server {start|stop|restart}"
exit 1
;;
esacДля запуска seahub как fastcgi измените переменную fastcgi на true.
Если используете MySQL, примените "mysql" в строке Required-Start:
# Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network mysqlЛоги:
mkdir /path/to/seafile/dir/logsДаём права на выполнение скрипта:
sudo chmod +x /etc/init.d/seafile-serverДобавляем seafile-server в rc.d:
sudo update-rc.d seafile-server defaultsДля RHEL/CentOS
Для RHEL/CentOS нужно использовать /etc/rc.local/ скрипты.
Определяем питон (python 2.6 или 2.7):
which python2.6 # or "which python2.7"В /etc/rc.local, добавляем директорию python2.6(2.7) в PATH, и добавляем seafile/seahub start:
`
# Assume the python 2.6(2.7) executable is in "/usr/local/bin"
PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin/
# Change the value of "user" to your linux user name
user=haiwen
# Change the value of "seafile_dir" to your path of seafile installation
# usually the home directory of $user
seafile_dir=/data/haiwen
script_path=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seafile.sh start > /tmp/seafile.init.log 2>&1
sudo -u ${user} ${script_path}/seahub.sh start > /tmp/seahub.init.log 2>&1Для запуска seahub как fastcgi измените "seahub.sh start" в конце на "seahub.sh start-fastcgi".
Для RHEL/CentOS как сервис
Используем /etc/init.d/ скрипты.
Создаём файл /etc/sysconfig/seafile:
# Change the value of "user" to your linux user name
user=haiwen
# Change the value of "seafile_dir" to your path of seafile installation
# usually the home directory of $user
seafile_dir=/data/haiwen
script_path=${seafile_dir}/seafile-server-latest
seafile_init_log=${seafile_dir}/logs/seafile.init.log
seahub_init_log=${seafile_dir}/logs/seahub.init.log
# Change the value of fastcgi to true if fastcgi is to be used
fastcgi=false
# Set the port of fastcgi, default is 8000. Change it if you need different.
fastcgi_port=8000Создаём скрипт /etc/init.d/seafile:
#!/bin/bash
#
# seafile
#
# chkconfig: - 68 32
# description: seafile
# Source function library.
. /etc/init.d/functions
# Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/network
if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/seafile ];then
. /etc/sysconfig/seafile
else
echo "Config file /etc/sysconfig/seafile not found! Bye."
exit 200
fi
RETVAL=0
start() {
# Start daemons.
echo -n $"Starting seafile: "
ulimit -n 30000
su - ${user} -c"${script_path}/seafile.sh start >> ${seafile_init_log} 2>&1"
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && touch /var/lock/subsys/seafile
return $RETVAL
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Shutting down seafile: "
su - ${user} -c"${script_path}/seafile.sh stop >> ${seafile_init_log} 2>&1"
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && rm -f /var/lock/subsys/seafile
return $RETVAL
}
#
# Write a polite log message with date and time
#
echo -e "\n \n About to perform $1 for seafile at `date -Iseconds` \n " >> ${seafile_init_log}
# See how we were called.
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart|reload)
stop
start
RETVAL=$?
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart}"
RETVAL=3
esac
exit $RETVALСоздаём скрипт /etc/init.d/seahub:
#!/bin/bash
#
# seahub
#
# chkconfig: - 69 31
# description: seahub
# Source function library.
. /etc/init.d/functions
# Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/network
if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/seafile ];then
. /etc/sysconfig/seafile
else
echo "Config file /etc/sysconfig/seafile not found! Bye."
exit 200
fi
RETVAL=0
start() {
# Start daemons.
echo -n $"Starting seahub: "
ulimit -n 30000
if [ $fastcgi = true ];
then
su - ${user} -c"${script_path}/seahub.sh start-fastcgi ${fastcgi_port} >> ${seahub_init_log} 2>&1"
else
su - ${user} -c"${script_path}/seahub.sh start >> ${seahub_init_log} 2>&1"
fi
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && touch /var/lock/subsys/seahub
return $RETVAL
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Shutting down seahub: "
su - ${user} -c"${script_path}/seahub.sh stop >> ${seahub_init_log} 2>&1"
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && rm -f /var/lock/subsys/seahub
return $RETVAL
}
#
# Write a polite log message with date and time
#
echo -e "\n \n About to perform $1 for seahub at `date -Iseconds` \n " >> ${seahub_init_log}
# See how we were called.
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart|reload)
stop
start
RETVAL=$?
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart}"
RETVAL=3
esac
exit $RETVALВключаем сервисы:
chmod 550 /etc/init.d/seafile
chmod 550 /etc/init.d/seahub
chkconfig --add seafile
chkconfig --add seahub
chkconfig seahub on
chkconfig seafile on
service seafile start
service seahub start